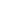
Aluminum composite tape is made of soft calendered aluminum foil laminated with polyester film which can provide high shielding coverage, make the signal away from electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference in a better manner. In this regard, it can be safely delivered to the terminal and provide shielding performance for the cable.
+86 18015848610
Application Scope:
It is widely used in coaxial cable and signal cable such as: HDMI USB RG-58, RG-6U, FTP, VGA, DVl and other kinds of electronic cables.
Color:
Natural, Gold, Red, Green, Blue, Black, Yellow
Tensile strength: > 60Mpa
Elongation: > 35%
Peeling strength: > 6.3N/cm
*The above data only shows the usual experimental data
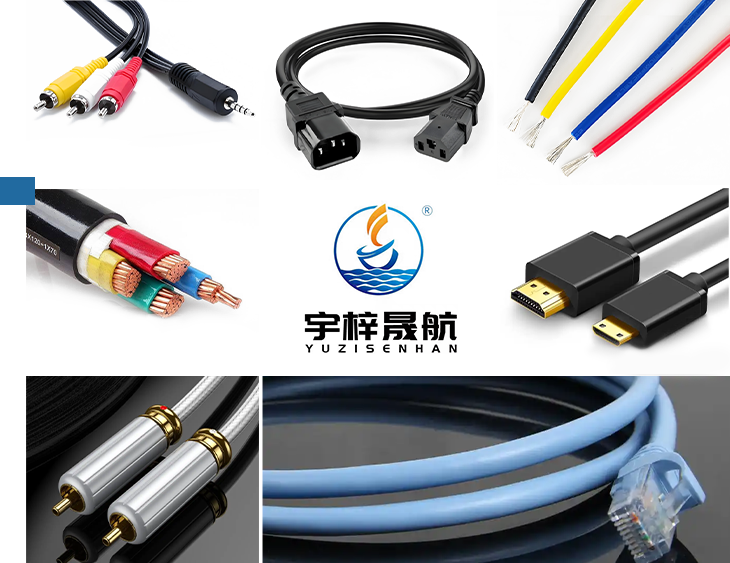
Structure
Single-sided aluminum foil Mylar tape


Product Parameters:
|
Structure |
Thickness |
Proportion (g/m²) |
Density (m²/kg) |
|
AL9 PET12 |
24 mic |
44 |
22.7 |
|
AL9 PET15 |
27 mic |
48 |
20.8 |
|
AL9 PET19 |
31 mic |
54 |
18.5 |
|
AL9 PET23 |
35 mic |
60 |
16.7 |
|
AL12 PET12 |
27mic |
53 |
18.9 |
|
AL12 PET15 |
30 mic |
57 |
17.5 |
|
AL12 PET! 9 |
34 mic |
62 |
16.1 |
|
AL12 PET23 |
38 mic |
68 |
14.7 |
|
AL12 PET36 |
51 mic |
88 |
11.4 |
|
AL15 PET19 |
37 mic |
70 |
14.3 |
|
AL25 PET12 |
40mic |
88 |
11.4 |
|
AL25 PET23 |
51 mic |
103 |
9.7 |
|
AL40 PET12 |
55 mic |
128 |
7.8 |
|
AL40 PET15 |
58 mic |
132 |
7.6 |
|
AL40 PET23 |
66 mic |
144 |
6.9 |
|
AL40 PET36 |
79 mic |
162 |
6.2 |
|
AL50 PET12 |
65 mic |
155 |
6.5 |
|
AL50 PET15 |
68 mic |
160 |
6.3 |
|
AL50 PET23 |
76 mic |
171 |
5.8 |
|
AL50 PET36 |
89 mic |
189 |
5.3 |
Product description:
Single-sided aluminum foil is an aluminum foil material that is coated or plated on only one side. One side is the original aluminum foil, and the other side is processed by special processes, such as coating with glue, painting or adding functional protective film. Single-sided aluminum foil is widely used in industry, construction and daily consumption due to its light weight, excellent thermal conductivity and shielding performance.
Product Features
High reflectivity: The smooth aluminum foil surface can effectively reflect heat and light, providing good thermal insulation and shielding performance.
Excellent barrier properties: It has excellent barrier effects on moisture, oxygen, light and chemical gases, extending the service life of the product.
Strong processability: Easy to cut, emboss, coat and compound with other materials.
Corrosion resistance and heat resistance: The anti-oxidation coating can protect the aluminum foil from corrosion and maintain its integrity at high temperatures.
Environmental protection: It can be recycled and meets environmental protection requirements.
Application fields and scenarios
1. Packaging industry
Food packaging: Used to make high-temperature resistant retort bags and frozen food packaging bags to keep the freshness of food and extend the shelf life.
Pharmaceutical packaging: used for blister packaging of medicines (such as tablets and capsules), blocking moisture and light to ensure drug stability.
2. Building and home
Thermal insulation materials: single-sided aluminum foil is used for building walls, roofs or pipe insulation layers, reflecting heat, energy saving and environmental protection.
Decorative materials: widely used as veneers or protective layers for home decoration, with aesthetics and functionality.
3. Electrical and electronic industries
Electromagnetic shielding: used for cable coating, electromagnetic interference shielding materials (EMI Shielding), to ensure stable operation of equipment.
Battery industry: used as current collector or outer packaging material in lithium batteries, lead-acid batteries and other fields.
4. Aerospace and automotive industries
Thermal insulation and noise reduction materials: aluminum foil is used for engine insulation layers of automobiles and aircraft to reduce noise and heat loss.
Protective coating: protect sensitive parts from moisture and corrosion.
5. Daily consumer goods
Kitchen foil: such as baking and grilling aluminum foil, high temperature resistance and high food safety.
Art and handicrafts: used to make crafts or models, easy to shape and bright and beautiful.
Reasons to choose single-sided aluminum foil
As a single-sided aluminum foil manufacturer, we can provide customized products according to customer needs, including material thickness, coating process, size specifications, etc.
Changzhou Yuzisenhan Electronic Co., Ltd.
Changzhou Yuzisenhan Electronic Co., Ltd. offer Single-sided aluminum foil. We are Single-sided aluminum foil Manufacturers and Single-sided aluminum foil Suppliers. Our company has a number of production lines: domestic copper-clad steel, copper-clad steel inlaid in line, and copper-clad aluminum manufacturing has the strength of one of the manufacturers.
Our company has advanced copper-clad steel, copper-clad aluminum, copper-clad steel inlay line production equipment, and professional testing instruments, in the selection of raw materials, the use of excellent raw materials; At the same time, a complete quality assurance system has been established to ensure that the company's products are subject to strict quality control from raw materials to finished products. Our company has passed the 1s09000:2000 quality management system certification.
Ask Our Experts For Free.
Please Give Us Your Questions And Suggestions. We Will Respond To Your Message In A Timely Manner.
Hot Products
News
-
industry news 2025-04-24
Copper Clad Aluminium Wire (CCA Wire) has become a popular choice for antenna systems due to its unique combination of lightweight prop...
View More -
industry news 2025-04-17
Copper clad steel wire (CCS wire) is a versatile and cost-effective solution for grounding systems in electrical and telecommunications...
View More -
industry news 2025-04-10
Copper coated steel wire (CCS wire) is a versatile and cost-effective material used in telecommunications, electrical grounding, and fe...
View More -
industry news 2025-04-03
Copper Clad Steel Wire: A Composite Material with Excellent PerformanceCopper Clad Steel Wire is a composite material that combines cop...
View More -
industry news 2025-03-27
1. The role of CCS WireCCS Wire is a key material used in battery connection systems to achieve electrical connections between cells an...
View More -
industry news 2025-03-20
According to the latest search results, the specific applications of CCA wire (Copper Clad Aluminum Wire) in the construction industry ...
View More
Single-sided aluminum foil Industry Knowledge
Single-sided aluminum foil vs. double-sided aluminum foil: Selection and cost comparison in industrial insulation materials
1. Basic definition and structural differences
Single-sided aluminum foil: only one side is covered with aluminum layer (usually smooth surface), and the other side is substrate (such as PET, PE, etc.), with asymmetric conductive/reflective properties.
Double-sided aluminum foil: both sides are covered with aluminum layer, symmetrical structure, both sides have conductive or reflective functions.
Key differences:
Conductivity: Double-sided aluminum foil can bidirectionally shield electromagnetic interference (EMI), while single-sided aluminum foil needs to rely on substrate insulation.
Heat reflection efficiency: Double-sided aluminum foil is suitable for bidirectional heat radiation environment (such as high-temperature pipelines), and single-sided aluminum foil is mostly used for unidirectional heat insulation (such as building walls).
2. Selection basis in industrial insulation materials
| Application Scenario | Single-sided Foil Advantages | Double-sided Foil Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cable Shielding | Lower cost, meets single-layer shielding requirements | More stable high-frequency signal shielding |
| Building Insulation | Aluminum side reflects heat outward, substrate adheres to walls | Bidirectional heat reflection, suitable for sandwich structures |
| EMI Protection for Electronics | Lightweight, suitable for internal localized shielding | Full-wrap shielding, higher protection grade |
| High-temperature Pipe Insulation | Single-sided bonding with anti-corrosion layers (e.g., fiberglass) | High-temperature resistant bidirectional reflection, reduces heat loss |
3. Cost comparison analysis
Material cost: Due to the increase in the amount of aluminum layer, the price of double-sided aluminum foil is usually 20%-30% higher than that of single-sided.
Processing cost:
Single-sided aluminum foil is easier to compound (such as combining with foam and fiber), and the process is simple;
Double-sided aluminum foil needs to consider the interlayer bonding strength, which may increase the cost of adhesives or coatings.
Life cycle cost:
Double-sided aluminum foil has better durability in harsh environments (such as chemicals and high temperatures) and low long-term maintenance costs;
Single-sided aluminum foil is significantly more economical in disposable packaging or short-term applications.
4. Industry trends and alternatives
Lightweight demand: Single-sided aluminum foil accounts for an increasing proportion of new energy vehicle battery insulation (weight reduction demand).
Environmental regulations: Double-sided aluminum foil is difficult to recycle, and some companies have turned to a combination of single-sided + degradable substrates.
Innovative materials: Nano-coated aluminum foil (single-sided functional optimization) may challenge the traditional double-sided aluminum foil market.
5. Selection recommendations
Prefer single-sided aluminum foil: cost-sensitive projects, one-way insulation/reflection scenarios (such as building roofs).
Prefer double-sided aluminum foil: high-frequency electromagnetic shielding, two-way thermal management or highly corrosive environments (such as petrochemical pipelines).

 EN
EN  English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى