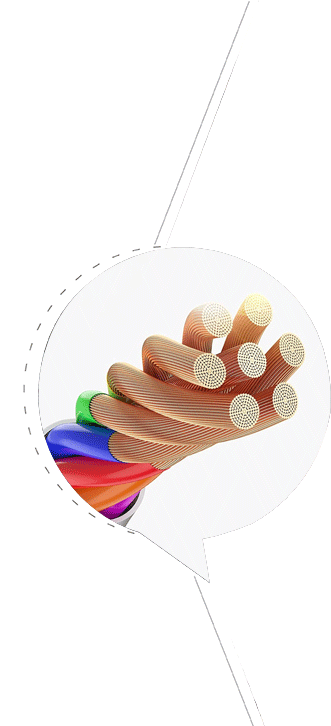
What factors affect the conductivity of CCA Wire?
The conductivity of CCA Wire is affected by the following factors:
Factors related to the copper layer
Thickness: Copper has better conductivity than aluminum. The thicker the copper layer, the closer the overall conductivity of the wire is to pure copper. More copper means more free electrons participating in the conduction, which can effectively reduce resistance and improve conductivity. For example, in situations where large currents need to be transmitted, increasing the thickness of the copper layer can reduce line heating and energy loss.
Uniformity: A uniform copper layer can evenly distribute the current on the surface of the wire to avoid increased resistance due to a thin copper layer in some areas. If the copper layer is uneven, the current will be concentrated in areas with thicker copper layers, causing local overheating, affecting the conductivity and wire life.
Factors related to aluminum core
Purity: A high-purity aluminum core has fewer impurities, less obstruction to the current, and can better assist the copper layer in conducting electricity. Impurities will scatter free electrons, increase resistance, and reduce conductivity. Therefore, the higher the purity of the aluminum core, the more conducive it is to improving the overall conductivity of CCA Wire.
Quality: The internal structure of high-quality aluminum core is dense and has few defects, which is conducive to current transmission. If the aluminum core has defects such as pores and cracks, it will destroy the current transmission path, increase resistance and reduce conductivity.
Production process factors
Annealing treatment: The appropriate annealing process can improve the crystal structure inside the wire, make the grains more uniform and refined, reduce lattice defects, thereby reducing resistance and improving conductivity. Wires that have not been well annealed have large internal stress and disordered crystal structure, which will affect the movement of free electrons and increase resistance.
Processing accuracy: Precise processing technology can ensure the close bonding between the copper layer and the aluminum core and reduce interface resistance. If the bonding is not tight, there are gaps or impurities, which will increase the resistance to current transmission and reduce conductivity. At the same time, high-precision processing can also ensure the uniformity of the wire diameter to avoid abnormal resistance due to local diameter changes.
What are the characteristics of CCA Wire's transmission performance at different frequencies?
The transmission performance of CCA Wire (copper clad aluminum wire) at different frequencies has the following characteristics:
At low frequencies
Resistance loss is dominant: At low frequencies, CCA Wire's transmission performance is similar to that of ordinary copper wires. The current is evenly distributed over the entire wire cross section, and the main energy loss comes from the resistance of the wire. At this time, the resistance of CCA Wire is relatively large, because aluminum is not as conductive as copper. Although it is wrapped with a copper layer, its overall resistance is still higher than that of pure copper wire. Therefore, when low-frequency and high-current transmission occurs, more heat may be generated, resulting in certain energy loss.
At high frequencies
Skin effect is significant: As the frequency increases, the skin effect becomes increasingly obvious. The skin effect refers to the fact that high-frequency currents are concentrated on the surface of the wire for transmission, while the current density inside the wire is relatively low. Since the copper layer of CCA Wire is located on the outer layer, it can better utilize the good conductivity of the copper layer at high frequencies, and the current is mainly transmitted in the copper layer, which to a certain extent makes up for the relatively poor conductivity of the aluminum core. However, compared with pure copper wire, the copper layer thickness of CCA Wire is usually thinner, so the transmission loss at high frequency will be slightly greater than that of pure copper wire, but it can still maintain good transmission performance.
Signal attenuation characteristics: In high-frequency applications, such as radio frequency communications, the signal attenuation of CCA Wire is related to factors such as frequency, transmission distance, and copper layer thickness. Generally speaking, the higher the frequency, the more serious the signal attenuation; the longer the transmission distance, the greater the signal attenuation. In addition, the thickness of the copper layer has an important influence on signal attenuation. A thicker copper layer can reduce the attenuation of the signal during transmission and improve the transmission quality of the signal. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to reasonably select parameters such as the copper layer thickness and wire diameter of CCA Wire according to specific frequency requirements and transmission distance factors to optimize the transmission performance and meet the needs of different high-frequency application scenarios.

 EN
EN  English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى